트랜잭션 추상화와 동기화를 통한 간편한 트랜잭션 적용
Application 구조
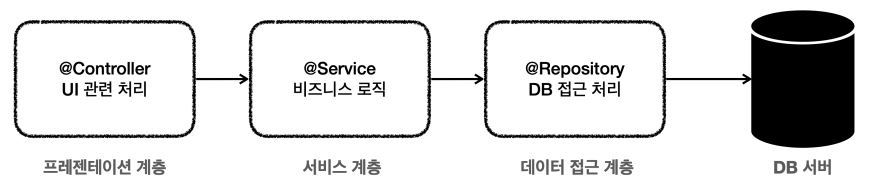
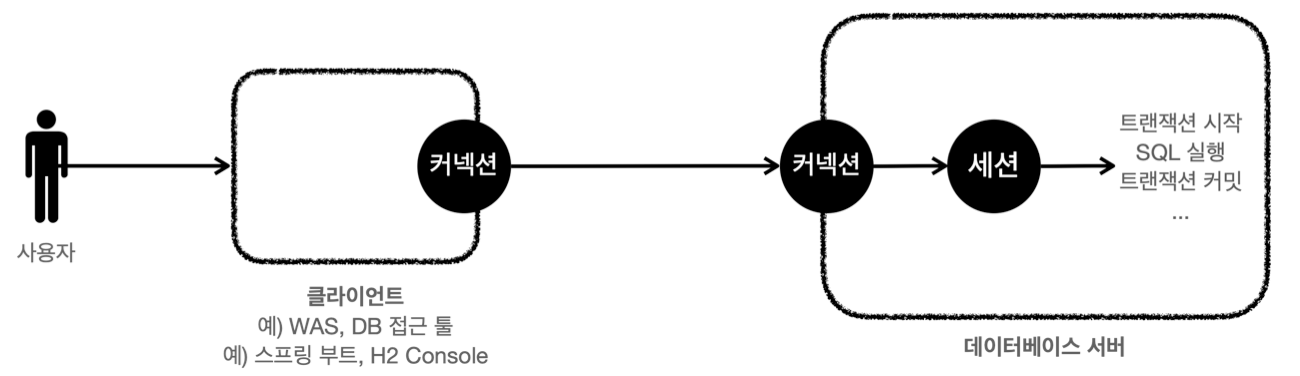
여러가지 애플리케이션 구조가 있지만, 가장 단순하면서 많이 사용하는 방법은 역할에 따라 아래 그림과 같이 3가지 계층으로 나누는 구조이다.
- 여기서 가장 중요한 곳은 어디일까? 바로 핵심 비즈니스 로직이 들어있는 서비스 계층이다. 시간이 흘러서 UI(웹) 와 관련된 부분이 변하고, 데이터 저장 기술을 다른 기술로 변경해도, 비즈니스 로직은 최대한 변경없이 유지되어야 한다.
- 비즈니스 로직의 순수성을 유지하기 위해서는 최대한 특정 기술 구현에 종속적이지 않게 개발해야 한다.
- Application 구조를 계증으로 나눈 이유도 서비스 계층을 최대한 수순하게 유지하기 위한 목적이다.
- 서비스 계층이 특정 기술에 종속되지 않아야 비즈니스 로직을 유지보수 하기도 쉽고, 테스트 하기도 쉽다.
1. 프레젠테이션 계층
- 프레젠테이션 계층은 클라이언트가 접근하는 UI와 관련된 기술인 Web, Servlet, HTTP 와 관련된 부분을 담당해줌으로서 서비스 계층을 UI와 관련된 기술로 부터 보호해준다.
- 예를들어 HTTP API 를 사용하다가 gRPC 같은 기술로 변경해도 프레젠테이션 계층 코드만 변경하고, 서비스 계층의 코도는 변경하지 않아도 된다.
2. 데이터 접근 계층
- 데이터 접근 계층은 데이터를 저장하고 관리하는 기술을 담당해주므로써,
JDBC,JPA와 같은 구체적인 데이터 접근 기술로부터 서비스 계층을 보호해준다. - 예를 들어서 JDBC를 사용하다가 JPA로 변경해도 서비스 계층은 변경하지 않아도 된다.
- 물론 서비스 계층에서 데이터 접근 계층을 직접 접근하는 것이 아니라, 인터페이스를 제공하고 서비스 계층은 이 인터페이스에 의존하는 것이 좋다. 그래야 서비스 코드의 변경 없이 JdbcRepository 를 JpaRepository 로 변경할 수 있다.
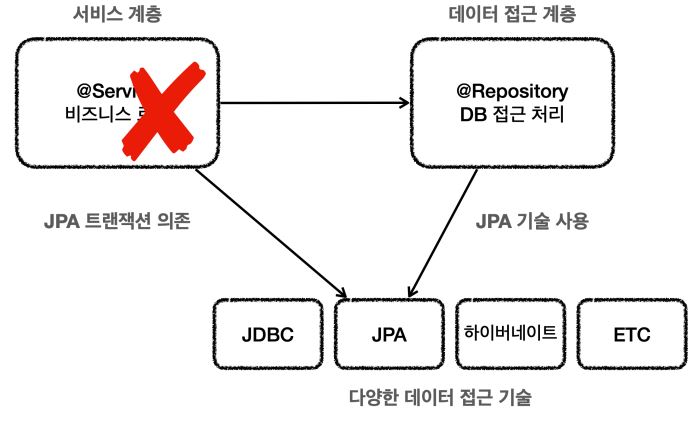
서비스 계층 Transaction 의 문제점
- 트랜잭션을 구현하기 위한 특정 기술 의존 문제(ex. JDBC, JPA …)
- 예외 누수 문제 (ex. SQLException)
- 반복되는 구현 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MemberServiceVer1 {
private final DataSource dataSource;
private final MemberRepositoryV2 memberRepository;
public void accountTransfer(String fromId, String toId, int money) throws SQLException {
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
try {
con.setAutoCommit(false); //트랜잭션 시작
//비즈니스 로직
bizLogic(con, fromId, toId, money);
con.commit(); //성공시 커밋
} catch (Exception e) {
con.rollback(); //실패시 롤백
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
} finally {
release(con);
}
}
private void bizLogic(Connection con, String fromId, String toId, int money) throws SQLException {
Member fromMember = memberRepository.findById(con, fromId);
Member toMember = memberRepository.findById(con, toId);
memberRepository.update(con, fromId, fromMember.getMoney() - money);
memberRepository.update(con, toId, toMember.getMoney() + money);
}
}
- 트랜잭션은 코드와 같이 비즈니스 로직이 있는 서비스 계층에서 시작하는 것이 좋다.
- 문제는 트랜잭션을 사용하기 위해서
javax.sql.DataSource,java.sql.Connection,java.sql.SQLException같은 JDBC 기술에 의존해야한다. - 위에 코드만 보더라도 트랜잭션을 적용하기 위해 JDBC 기술에 의존하며, JDBC를 사용해 트랜잭션을 처리하는 코드가 많아 졌다.
- 이러한 코드 방향은 JDBC에서 JPA 같은 다른 기술로 바뀌게 되면 서비스 코드도 모두 함께 변경해야 하는 상황이 발생하고, 이런식의 개발은 유지보수성을 망치는 길이다.
- 추가적으로
try-catch-finally, DB 연동 과정 등의 반복되는 코드들도 문제이다.
Transaction의 추상화
앞서 구현한 서비스 계층은 트랜잭션을 사용하기 위해 JDBC 기술에 의존하고 있기 때문에 JDBC -> JPA 로 데이터 접근 기술을 변경하게 되면 서비스 계층의 트랜잭션 관련 코드는 전면 수정되어야 할 것이다.
데이터 접근 기술에 따른 트랜잭션 사용법
- JDBC: connection.setAutoCommit(false)
- JAP: transaction.begin();
- 두 기술 뿐만이 아니라 향후 어떤 기술도 사용법이 서로 다를 것이다.
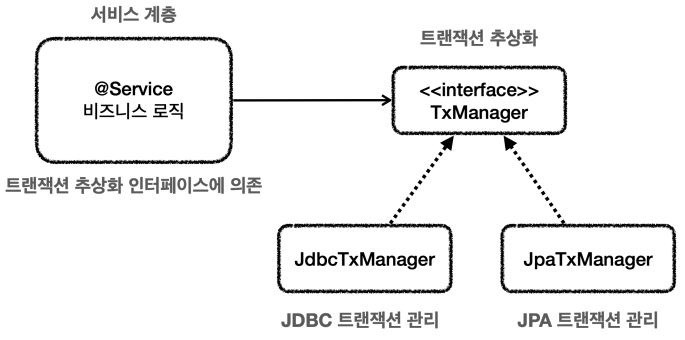
트랜잭션 추상화 인터페이스
이런 서비스계층의 의존문제를 해결하려면 트랜잭션 기능을 추상화하면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
public interface TransactionManager {
begin();
commit();
rollback();
}
트랜잭션을 단순하게 생각하자면, 트랜잭션을 시작하고 비즈니스 로직의 수행이 끝나면 커밋하거나 롤백하면 된다. 해당 인터페이스를 기반으로 각각의 데이터 접근 기술에 맞는 구현체를 만들기만 하면 될 것이다.
- JdbcTransactionManager : JDBC 트랜잭션 기능을 제공하는 구현체
- JpaTransactionManager: JPA 트랜잭션 기능을 제공하는 구현체
- 서비스는 특정 트랜잭션 기술에 직접 의존하는 것이 아니라 TransactionManager 라는 추상화된 인터페이스에 의존한다. 이제 개발 상황에 맞게 원하는 트랜잭션 매니저 구현체를 DI 를 통해 주입하면 된다.
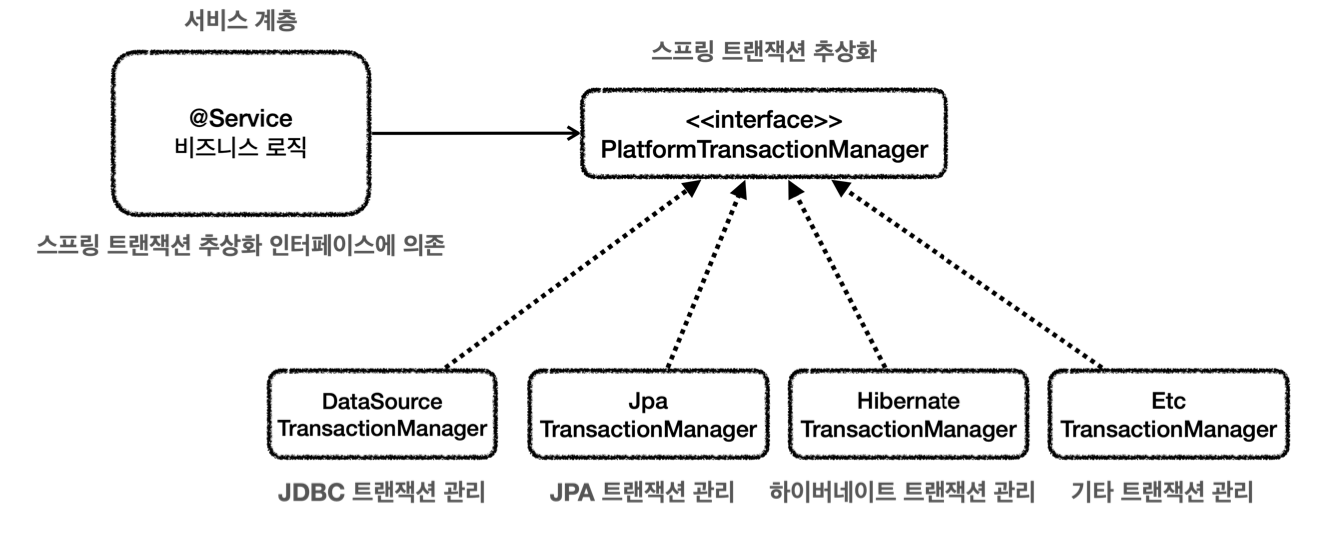
스프링의 트랜잭션 추상화
사실 스프링은 이미 이런 상황에 대해 고미한고 대비 해두었기 때문에 스프링이 제공하는 트랜잭션 추상화 기술을 사용하면 된다. 심지어 데이터 접근 기술에 따라 트랜잭션 구현체도 대부분 만들어두었다.
스프링 트랜잭션 추상화의 핵심은 PlatformTransactionManager 인터페이스이다.
1
- `org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager`
1
2
3
4
5
6
package org.springframework.transaction;
public interface PlatformTransactionManager extends TransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}
getTransaction(): 트랜잭션을 시작한다.- 이름이
getTransaction()인 이유는 기존에 이미 진행중인 트랜잭션이 있는 경우 해당 트랜잭션에 참여할 수 있기 때문이다. - 동일한 커넥션에서 이미 생성된 트랜잭션이 있는 경우 새 트랜잭션을 시작하지 않는다.
- 이름이
commit(): 트랜잭션을 커밋한다.rollback(): 트랜잭션을 롤백한다.
트랜잭션 동기화
스프링이 제공하는 트랜잭션 매니저는 크게 2가지 역할을 한다.
PlatformTransactionManager 인터페이스 구현체를 트랜잭션 매니저라 한다.
- 트랜잭션 추상화
- 리소스 동기화
트랜잭션 추상화는 앞서 설명하였고, 리소스 동기화에 대해 얘기 하자면 트랜잭션을 유지하려면 트랜잭션의 시작부터 끝까지 같은 DB Connection 을 유지해야한다. 결국 같은 커넥션을 동기화 하기 위해서 파라미터를 통해 Repository 로 Connection 을 전달하는 방법을 사용하였다. 이러한 방식은 커넥션을 전달하기 위해 코드가 지저분해지고, 중복된 코드를 작성하게 되는 문제가 발생한다.
스프링은 트랜잭션 동기화 매니저를 제공해주는데, 쓰레드로컬(Thread Local) 을 사용해서 커넥션을 동기화 해준다. 트랜잭션 매니저는 내부적으로 트랜잭션 동기화 매니저를 사용한다. 트랜잭션 동기화 매니저는 쓰레드 로컬을 사용하기 때문에 멀티쓰레드 상황에 안전하게 커넥션을 동기화 할 수 있다. 따라서 커넥션이 필요하다면 트랝개션 동기화 매니저를 통해 커넥션을 획득하면 됨으로, 더이상 파라미터를 통해 Connection 을 전달할 필요가 없어진다.
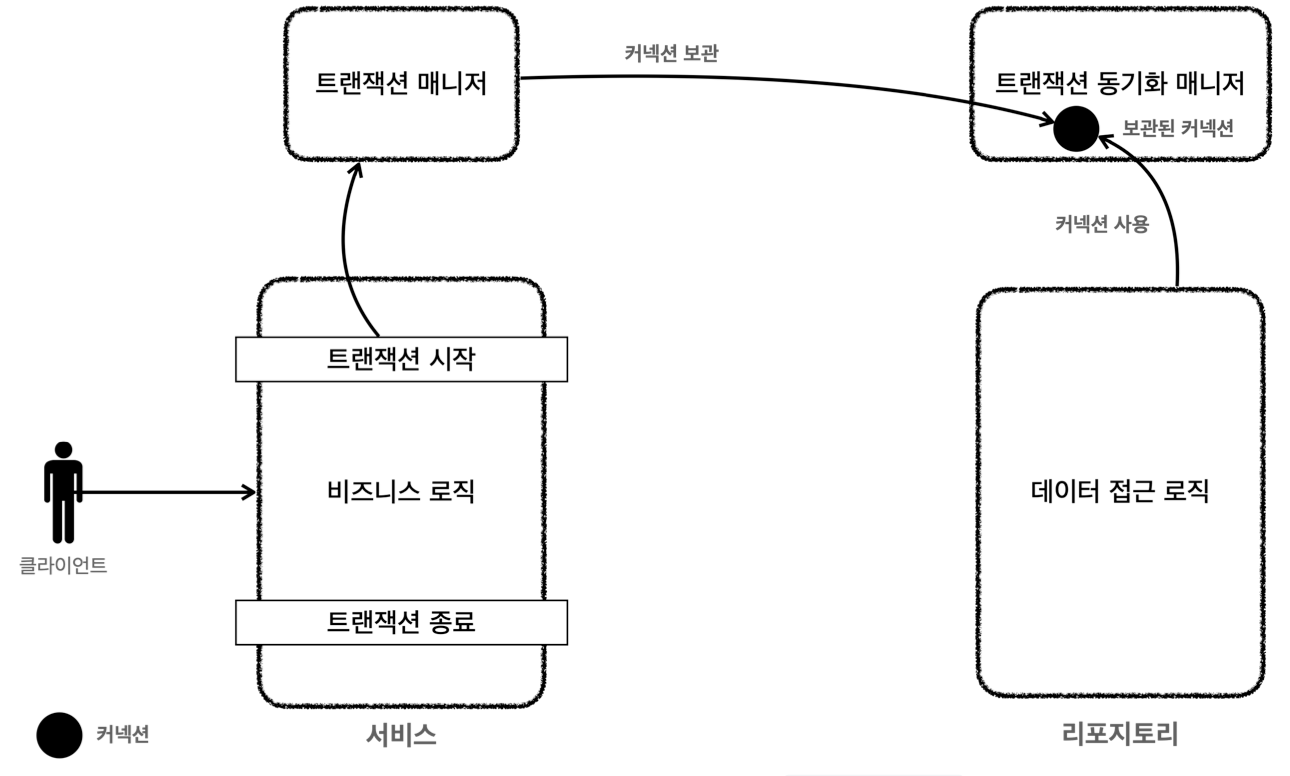
트랜잭션 동기화 동작 방식
- 트랜잭션 매니저는 데이터소스를 통해 커넥션을 만들고 트랜잭션을 시작
- 트랜잭션 매니저는 트랜잭션이 시작된 커넥션을 트랜잭션 동기화 매니저에 보관
- Repository는 트랜잭션 동기화 매니저에 보관된 커넥션을 꺼내서 사용
- 트랜잭션이 종료되면 트랜잭션 매니저는 트랜잭션 동기화 매니저에 보관된 커넥션을 통해 트랜잭션을 종료하고, 커넥션을 닫음
트랜잭션 동기화 매니저 클래스를 열어보면 쓰레드 로컬을 사용하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
import hello.jdbc.domain.Member;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceUtils;
import org.springframework.jdbc.support.JdbcUtils;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* 트랜잭션 - 트랜잭션 매니저
* DataSourceUtils.getConnection()
* DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection() */
@Slf4j
public class MemberRepositoryV3 {
private final DataSource dataSource;
public MemberRepositoryV3(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
public Member save(Member member) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into member(member_id, money) values(?, ?)";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, member.getMemberId());
pstmt.setInt(2, member.getMoney());
pstmt.executeUpdate();
return member;
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, null);
}
}
private void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(resultSet);
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(statement);
/**
* - connection.close() 를 해버린다면 커넥션이 유지되지 않는 문제가 발생한다.
* - 해당 커넥션은 트랜잭션 종료(커밋 / 롤백) 할 때 까지 살이있어야 한다.
*/
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(connection, dataSource);
}
private Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
/**
* - 트랜잭션 동기화 매니저가 관리하는 커넥션이 있으면 해당 커넥션을 반환한다.
* - 따로 관리하는 커넥션이 없다면 새로운 커넥션을 반환한다.
*/
Connection connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(dataSource);
log.info("get connection={} class={}", connection, connection.getClass());
return connection;
}
}
- DataSourceUtils.getConnection()
- 트랜잭션 동기화 매니저가 관리하는 커넥션이 있으면 해당 커넥션을 반환
- 따로 관리하는 커넥션이 없다면 새로운 커넥션 생성후 반환
- DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection()
- 예전처럼 connection.close() 를 통해 직접 커넥션을 닫아버리면 커넥션이 트랜잭션을 종료하기 전까지 유지되지 않는 문제가 발생한다. 한 커넥션은 트랜잭션 종료(커밋 / 롤백) 할 때 까지 살아있어야 한다.
- releaseConnection()에 커넥션을 주면 트랜잭션을 사용하기 위해 동기화된 커넥션은 닫지 않고 그대로 유지해준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
import hello.jdbc.domain.Member;
import hello.jdbc.repository.MemberRepositoryV3;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.DefaultTransactionDefinition;
/**
* 트랜잭션 - 트랜잭션 매니저
*/
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MemberServiceV3_1 {
private final PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager;
private final MemberRepositoryV3 memberRepository;
public void accountTransfer(String fromId, String toId, int money) throws IllegalStateException {
// 트랜잭션 시작
TransactionStatus transactionStatus = platformTransactionManager.getTransaction(new DefaultTransactionDefinition());
try {
// 비즈니스 로직
Member fromMember = memberRepository.findById(fromId);
Member toMember = memberRepository.findById(toId);
int fromMemberMoney = fromMember.getMoney() - money;
int toMemberMoney = toMember.getMoney() + money;
memberRepository.update(fromId, fromMemberMoney);
validation(toMember);
memberRepository.update(toId, toMemberMoney);
// 성공시 커밋
platformTransactionManager.commit(transactionStatus);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 실패시 롤백
platformTransactionManager.rollback(transactionStatus);
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
private void validation(Member toMember) {
if (toMember.getMemberId().equals("ex")) {
throw new IllegalStateException("이체중 예외 발생");
}
}
}
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager- 트랜잭션 매니저 주입
transactionManager.getTransaction()- 트랜잭션을 시작하고,
TransactionStatus를 반환한다. - 이후 트랜잭션 커밋/롤백할 때 사용된다.
- 트랜잭션을 시작하고,
transactionManager.commit(status)/ransactionManager.rollback(status)
트랜잭션 템플릿
트랜잭션을 사용하는 로직을 보면 같은 패턴이 반복되고 있음을 확인할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
TransactionStatus status = transactionManager.getTransaction(newDefaultTransactionDefinition());
try {
//비즈니스 로직
bizLogic(fromId, toId, money);
transactionManager.commit(status); //성공시 커밋
} catch (Exception e) {
transactionManager.rollback(status); //실패시 롤백
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
- 트랜잭션 시작 -> 비즈니스로직 실행 -> 커밋 / 롤백
- 서비스마다 트랜잭션을 적용해 비즈니스 로직을 시작하려면 try - catch - finally 구조가 매번 반복될 것이다.
- 이런 무의미한 반복 코드 구조를 템플릿 콜백 패턴을 활용하면 깔금하게 해결할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
public class TransactionTemplate {
private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
public <T> T execute(TransactionCallback<T> action){..}
void executeWithoutResult(Consumer<TransactionStatus> action){..}
}
- 스프링은
TransactionTemplate이라는 템플릿 클래스를 제공한다. execute(): 응답 값이 있을 때 사용executeWithoutResult(): 응답 값이 없을 때 사용
트랜잭션 템플릿 적용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
import hello.jdbc.domain.Member;
import hello.jdbc.repository.MemberRepositoryV3;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 트랜잭션 - 트랜잭션 템플릿
*/
@Slf4j
public class MemberServiceV3_2 {
private final TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
private final MemberRepositoryV3 memberRepository;
public MemberServiceV3_2(PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager, MemberRepositoryV3 memberRepository) {
this.transactionTemplate = new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager);
this.memberRepository = memberRepository;
}
public void accountTransfer(String fromId, String toId, int money) throws IllegalStateException {
/**
* # 트랜잭션 템플릿
* - 템플릿 형태를 적용하므로써 (트랜잭션 시작 / 성공 커밋 / 실패 롤백) 과정을 생략 처리 할 수 있다.
* - 하지만 여전히 서비스 계층임에도 불구하고 트랜잭션 처리 로직은 남아있다.
* - AOP 의 Proxy 를 도입한다면 서비스 클래스를 순수한 비즈니스 로직으로만 구성이 가능해 질 것이다.
*/
transactionTemplate.executeWithoutResult((status) -> {
try {
// 비즈니스 로직
Member fromMember = memberRepository.findById(fromId);
Member toMember = memberRepository.findById(toId);
int fromMemberMoney = fromMember.getMoney() - money;
int toMemberMoney = toMember.getMoney() + money;
memberRepository.update(fromId, fromMemberMoney);
validation(toMember);
memberRepository.update(toId, toMemberMoney);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
});
}
private void validation(Member toMember) {
if (toMember.getMemberId().equals("ex")) {
throw new IllegalStateException("이체중 예외 발생");
}
}
}
- 트랜잭션 템플릿을 이용해 반복되는 코드 제거하였다.
TransactionTemplate을 사용하려면transactionManager가 필요하기 때문에 생성자에서transactionManager를 주입 받으면서TransactionTemplate을 생성하였다.- 트랜잭션 템플릿 덕분에 트랜잭션을 시작하고, 커밋하거나 롤백하는 코드가 모두 제거되었다.
- 코드에서 예외를 처리하기 위해
try~catch가 들어갔는데,bizLogic()메서드를 호출하면SQLException체크 예외를 넘겨준다. 해당 람다에서 체크 예외를 밖으로 던질 수 없기 때문에 언체크 예외로 바꾸어 던지도록 예외를 전환했다.
트랜잭션 템플릿 적용의 한계
지금까지 트랜잭션 적용을 위해 트랜잭션 추상화, 트랜잭션 동기화, 트랜잭션 템플릿을 도입했다. 이로써 코드의 복잡함이나 비효율적인 코드의 반복은 없앨수 있었지만 결과적으로 아직 Service Layer 에 순수한 비즈니스 로직만 남기는 원칙에 적합하지 않다.
이러한 서비스계층의 순수함을 지키기 위해서는 스프링의 AOP를 통한 프록시를 도입해서 해결해야한다.